Search results: 266
First yr one credit course on design thinking
- Teacher: Mr. Nand Kishor Yadav [CSE]
Design Thinking
This file Contains all the details
Course Objectives
1. To help Student understand the concept of Digital Marketing & E-commerce in today’s scenario
2. To enable student in creating and maintaining a good website and blog posts.
3. To make student understand the importance of SEO and Email Marketing in today’s modern world
4. To understand the functioning and importance of Social Media Marketing via various platforms
5. To understand various Analytics tools of online marketing

|
Pre-requisite: |
|
Course Objectives: |
|
|
Course Outcome: |
|
Distributed systems is the study of how to build a computer system where the state of the program is divided over more than one machine (or "node"). This course is in active development.

DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM. CODE: MPH 102 T
Drug Delivery System course is designed to impart knowledge on the area of advances in novel drug delivery systems. Upon completion of the Drug Delivery System course, student shall be able to understand
§ The various approaches for development of Novel Drug Delivery Systems.
§ The criteria for selection of drugs and polymers for the development of delivering system.
§ The formulation and evaluation of Novel Drug Delivery Systems.

- Teacher: DR.N.G.RAGHAVENDRA RAO [KSOP]
Data Structure Lab
2023-24
Section A2
BCS351

- Teacher: Dr. HARSH KHATTER [CO]
- Teacher: Mr. Pardeep Tyagi [CO]
- Teacher: MR. ANURAG MISHRA [CS]
- Teacher: MR. SREESH GAUR [CS]
Electrical Machine Lab EEE 2nd Year
1. Describe the fundamentals of circuit switching and distinguish complex telephone systems.
2. Differentiate the fundamentals of Space division switching and time division switching.
3. Design, develop and evaluate the telecom traffic to meet defined specifications and needs.
4. Identify the control of switching networks and signalling concepts.
5. Classify the engineering concepts of packet switching and routing which will help to design various switch architectures for future research work.
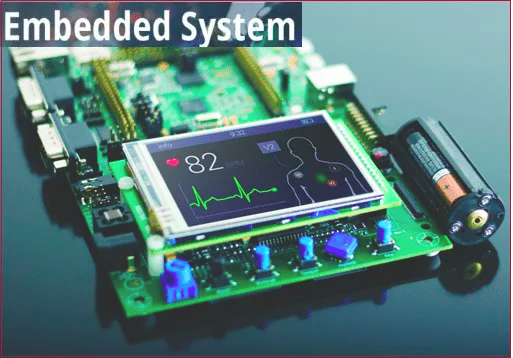
An embedded system is a microprocessor-based computer hardware system with software that is designed to perform a dedicated function, either as an independent system or as a part of a large system. At the core is an integrated circuit designed to carry out computation for real-time operations.
Complexities range from a single microcontroller to a suite of processors with connected peripherals and networks; from no user interface to complex graphical user interfaces. The complexity of an embedded system varies significantly depending on the task for which it is designed.
Embedded system applications range from digital watches and microwaves to hybrid vehicles and avionics. As much as 98 percent of all microprocessors manufactured are used in embedded systems.
This course is specially designed for the first year Engineering students. It comprises of basic understanding of Electronics Engineering and their application in modern day technology.
UNIT-1: Energy Scenario: Classification of Energy, Indian energy scenario, Sectorial energy
consumption (domestic, industrial and other sectors), energy needs of growing economy, energy
intensity, long term energy scenario, energy pricing, energy security, energy conservation and its
importance, energy strategy for the future.
Energy Conservation Act 2001 and related policies: Energy conservation Act 2001 and its
features, notifications under the Act, Schemes of Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) including
Designated consumers, State Designated Agencies, Electricity Act 2003, Integrated energy policy,
National action plan on climate change, ECBC code for Building Construction.
UNIT-2: Demand Side Management (DSM): Concept and Scope of Demand Side Management,
Difference between Energy Efficiency and DSM, Evolution of Demand Side Management, DSM
Strategy, Planning, Implementation and its application, Customer Acceptance & its implementation
issues, National and International Experiences with DSM, UDAY scheme and other government
initiatives for DISCOMs.
Energy Monitoring and Targeting: Defining monitoring & targeting, elements of monitoring &
targeting, data and information-analysis, techniques –energy consumption, production, cumulative
sum of differences (CUSUM). Energy Management Information Systems (EMIS)
UNIT-3: Energy Audit: Aim of energy Audit, Strategies of Energy Audit, Energy management
Team Consideration in implementing energy conservation Programme, Process flow diagram, Energy
Audit report format, Benchmarking and Energy Performance, Instruments for energy audit, Economic
analysis.
UNIT-4: System Audit of Mechanical Utilities: Pumps, types and application, unit’s assessment,
improvement option, parallel and series operating pump performance. Energy Saving in Pumps &
Pumping Systems. Bloomers (Blowers) types & application, its performance assessment, series &
parallel operation applications & advantages. Energy Saving in Blowers Compressors, types &
applications, specific power consumption, compressed air system & economic of system changes.
Energy Saving in Compressors & Compressed Air Systems Cooling towers, its types and
performance assessment & limitations, water loss in cooling tower. Case studies related to Energy
Audit & Management in Industries
UNIT-5: Energy Efficient Technology: Need for Energy Efficient Devices, Life Cycle Assessment,
Comparison between simple pay-back and life cycle cost assessment, Energy Efficient Motors-motor
losses and loss reduction techniques, determining and comparing motor efficiencies, motor efficiency
testing standards, BIS specification for Energy Efficient Motors, efficiency as a function of load,
Energy Efficient Lighting Sources-compact fluorescent lamp, light emitting diode, LED lamp, role of
voltage on the efficiency of lighting system, Importance of Automatic power factor controllers,
Variable Frequency Drives.
Course Objectives:
1. To facilitate software based learning to provide the required English Language proficiency to students.
2. To acquaint students with specific dimensions of communication skills i.e. Reading, Writing, Listening, Thinking and Speaking.
3. To train students to use the correct and error-free writing by being well versed in rules of English grammar.
4. To cultivate relevant technical style of communication and presentation at their work place and also for academic uses.
5. To enable students to apply it for practical and oral presentation purposes by being honed up
in presentation skills and voice-dynamics.
Course Objectives:
1. To facilitate software based learning to provide the required English Language proficiency to students.
2. To acquaint students with specific dimensions of communication skills i.e. Reading, Writing, Listening, Thinking and Speaking.
3. To train students to use the correct and error-free writing by being well versed in rules of English grammar.
4. To cultivate relevant technical style of communication and presentation at their work place and also for academic uses.
5. To enable students to apply it for practical and oral presentation purposes by being honed up
in presentation skills and voice-dynamics.
Course Objectives:
1. The purpose of this course is to expose the student to the basic concepts of entrepreneurship and Common myths to becoming an entrepreneur. Students will be exposed to the functions of entrepreneurs, and problems faced by them in the real world.
2. To impart an understanding of Entrepreneurial Finance, Assistance, and the role of Entrepreneurial Development Agencies
3. To provide insights to students in converting an Idea to an opportunity and develop understanding of various funding sources for a startup.
4. Familiarizing the students on Developing a Business Plan.
5. To provide a basic understanding of Launching a New Venture
open elective for VI semester
- Teacher: DR DILKESHWAR PANDEY [CSE]
- Teacher: Mr. Vipin Deval [CSE]
- Teacher: Ms. Shivangi Tyagi [CSIT]
The course provides information various export import policies; rules and regulations; essential documentation; strategies for improving the efficiency of the work force, market presence and enhance product marketing and sale. Who Should Attend:- ❖ Candidates who start a new business in the field of import export.

Demonstrate the knowledge of the basic structure, components, features and
generations of computers. Describe the concept of computer languages, language translators and construct
algorithms to solve problems using programming concepts. Compare and contrast features, functioning & types of operating system and
computer networks. Demonstrate architecture, functioning & services of the Internet and basics of
multimedia. Illustrate the emerging trends and technologies in the field of Information
Technology.
