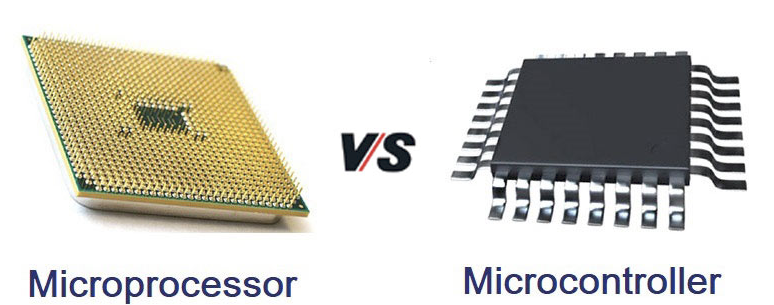
A microcontroller is a compact integrated circuit designed to govern a specific operation in an embedded system. A typical microcontroller includes a processor, memory and input/output (I/O) peripherals on a single chip.

Human values are the virtues that guide us to take into account the human element when we interact with other human beings. Human values are, for example, respect, acceptance, consideration, appreciation, listening, openness, affection, empathy and love towards other human beings.

The microcontroller is designed for a specific task or to perform the assigned task repeatedly. Once the program is embedded on a microcontroller chip, it can’t be altered easily and you may need some special tools to reburn it. As per application, the process is fixed in microcontroller. Hence, the output depends on the input given by the user or sensors or predefined inputs.
The microprocessor is useful in very intensive processes. It only contains a CPU (central processing unit) but there are many other parts needed to work with the CPU to complete a process. These all other parts are connected externally.
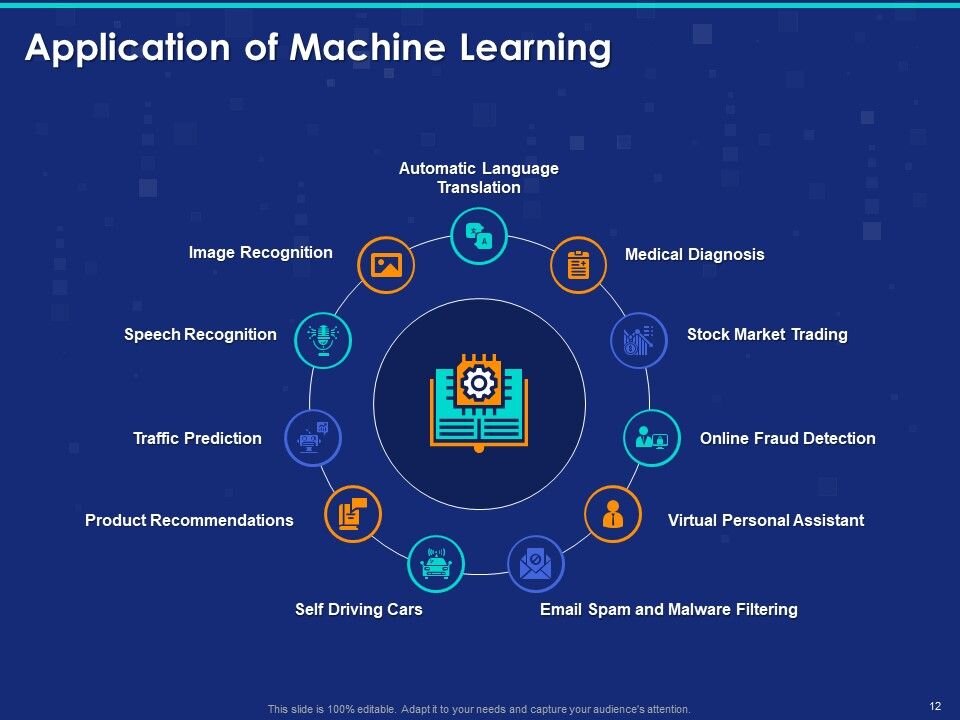
Machine learning (ML) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows software applications to become more accurate at predicting outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms use historical data as input to predict new output values.
Recommendation engines are a common use case for machine learning. Other popular uses include fraud detection, spam filtering, malware threat detection, business process automation (BPA) and predictive maintenance.
Why is machine learning important?
Machine learning is important because it gives enterprises a view of trends in customer behavior and business operational patterns, as well as supports the development of new products. Many of today's leading companies, such as Facebook, Google and Uber, make machine learning a central part of their operations. Machine learning has become a significant competitive differentiator for many companies.
This file Contains all the details
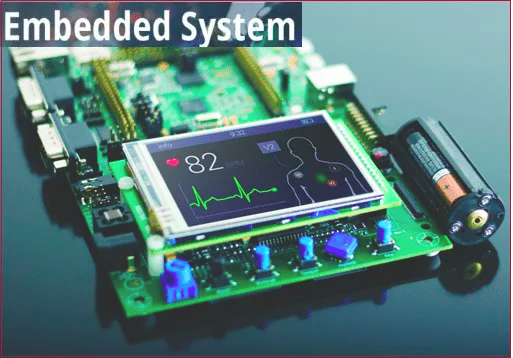
An embedded system is a microprocessor-based computer hardware system with software that is designed to perform a dedicated function, either as an independent system or as a part of a large system. At the core is an integrated circuit designed to carry out computation for real-time operations.
Complexities range from a single microcontroller to a suite of processors with connected peripherals and networks; from no user interface to complex graphical user interfaces. The complexity of an embedded system varies significantly depending on the task for which it is designed.
Embedded system applications range from digital watches and microwaves to hybrid vehicles and avionics. As much as 98 percent of all microprocessors manufactured are used in embedded systems.
COURSE OBJECTIVE: Students undergoing this course are expected:
1. To understand the concept ofuniversal op-amp based biquad.
2. To analyseamplitude control or stabilization applied to any sinusoidal oscillators and Op-amp/ OTA based function generator.
3. To design log/antilog circuits and find applications of analog multiplier/ divider.
4. To learn digital system design and its hardware implementation using TTL/ CMOS ICs and Any circuit idea using 555 Timer.
5. To design the circuit, Make hardware and measure various parameters and Simulation in Spice of the
designed circuit.
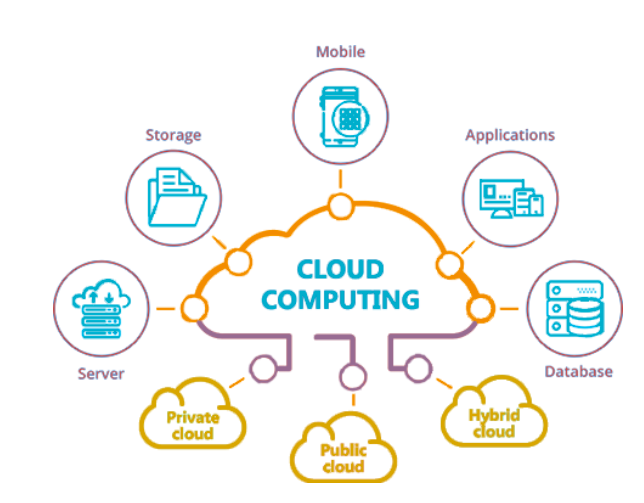
Cloud Computing is a large-scale distributed computing paradigm which has become a driving
force for information technology over the past several years. The exponential growth data size
in scientific instrumentation/simulation and social media has triggered the wider use of cloud
computing services. We will explore solutions and learn design principles for building large
network-based systems to support both compute and data intensive computing across
geographically distributed infrastructure.